Learn everything you need to know about the keto diet with an easy-to-follow keto meal plan. Our keto diet plan for beginners has 3 weeks of meals including easy dinner ideas, breakfast ideas, lunch ideas, healthy snacks and dessert recipes. Get into ketosis and start burning fat faster than ever!

Jump to:
- Introduction to keto
- What Is A Keto Diet?
- Keto Diet Plan
- How the Keto Diet Works
- Foods to Eat on Keto
- Foods to Avoid on Keto
- Essential Groceries List
- Exercising on the Keto Diet
- Dining Out Tips on Keto
- Benefits of a Keto Diet
- Keto Meal Plan Breakdown
- The First 5 Days Of Keto
- Stage 1: Week 1 (Days 1-5)
- Stage 2: Week 2 (Days 6-12)
- Stage 2: Week 3 (Days 13-19)
- Final Remarks
- 💬 Reviews
Introduction to keto
I have to tell you about this ketogenic diet, or as you may have heard of it, "The Keto Diet."
Every day, you hear about a new diet for longevity and excellent health: Atkins, paleo, vegan, gluten-free, fruitarian, you name it.
It's always hard to navigate which of these diets is best, and often, there isn't enough information to base your decision on.
Today, I'll introduce you to the ketogenic diet, which helps to burn fat quickly for fast weight loss results.
At the end of the article, you'll find a free keto meal plan with recipes for breakfast, lunch, dinner, dessert, and snacks! I recommend reading the entire article because it covers everything you need to know about the keto diet for beginners.
What Is A Keto Diet?
Can you believe the keto diet started over 90 years ago to cure epilepsy in children?
It did start to lose its impact after a few years as companies created new medicines and released them onto the market.
But would you believe Mother Nature was doing a better job relieving epilepsy than the new medications?
Maybe that is why it started to become popular again around 1994.
It became noticeable again when a young Charlie Abraham made an astonishing recovery from epilepsy seizures he had daily. His family was so happy with these results that they started "The Charlie Foundation."
Nothing had worked no matter what they had tried previously with the keto diet.
Charlie had been following a keto diet plan for five years, and then his seizures stopped.
Some studies have shown that following a keto meal plan can improve and slow diabetes, Parkinson's, polycystic ovaries, and dementia. (1, 2, 3, 4).
In this article, I will explain how you can benefit from the keto diet to lose weight and transform your life.
Keto Diet Plan
Like many other diets, the keto diet has a very low-carb intake.
It is these carbohydrates that provide the glucose that our bodies use to produce energy. Carbohydrates are the body's primary source of energy. They also help supply feel-good chemicals to the brain that stimulate the pleasure centers.
Eating high-carb foods makes us happy. That is why we crave them so much! However, carbs are one of the main foods responsible for weight gain and health issues.
They may give us a quick boost in energy and stimulate the brain's pleasure centers, but there is one significant downside: any carbs the body has not used to produce energy get stored, and you guessed it, they get stored as fat!
Now, you may be thinking - if carbs provide the energy, and we are about to consume fewer carbs, where will our body get energy from?
Remember all those left-over carbs stored as fat, probably sitting on your belly?
FAT! Fat will be the body's new energy source instead of carbohydrates.
How the Keto Diet Works
The keto diet principles are simple: we reduce carbohydrate intake and increase fat and protein intake. It requires tracking, but don't worry too much about counting calories. The most important thing is to break up the calories you're consuming into three categories:
Keto Macros Breakdown

- 70-75% of your calories will consist of fat
- 20-25% of your calories will consist of protein
- 5% of your calories will consist of carbs
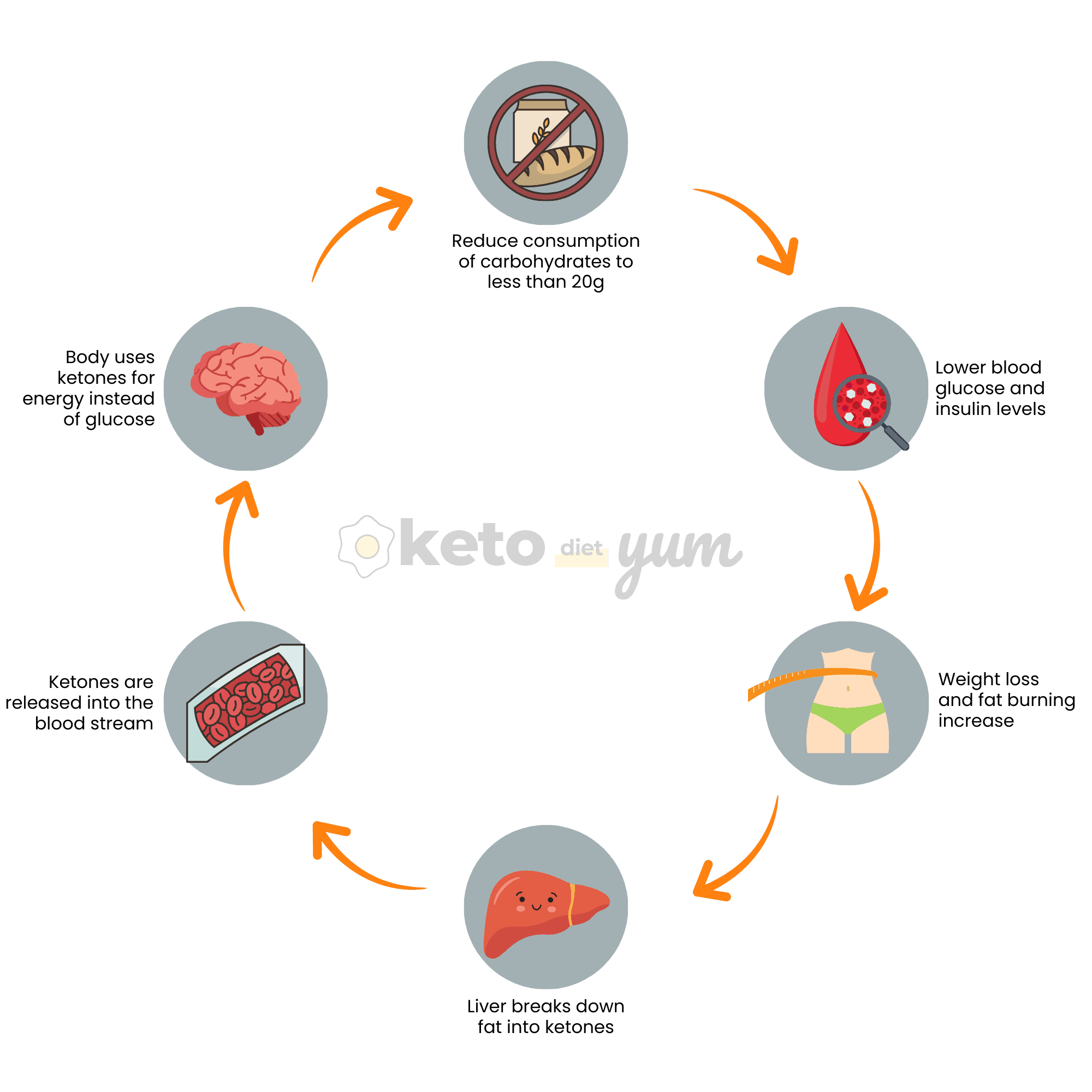
When you stick to these ratios, the body will enter a state of ketosis. Ketosis occurs when there aren't enough carbohydrates to burn for energy, so the body burns fat.
In ketosis, the body burns ketones to produce energy rather than carbs. This simple process will lead us to weight loss and better health.
So, the primary purpose of the keto diet is to keep your body in a state of ketosis to burn excess fat constantly.
70-75% of the diet is from fats - is that a typo?!
There are no typos here! Fat, including saturated fat, has no effect on blood sugar, which keeps the body in a solid state of ketosis.
Carbs are the true culprit of driving up blood sugar, spiking insulin, and converting straight to fat.
Even though you'll increase your saturated fat intake, the low carbohydrate diet will help lower triglycerides, resulting in a better metabolic panel.
Studies have shown that over three months on a keto diet, cholesterol numbers looked better on average than off of it. Pretty cool!
Continuing...
I want to mention that some diets similar to this are pretty famous. Maybe you've heard of the Atkins Diet?
Well, at least with the keto diet, it is backed up with scientific evidence gathered over nearly 100 years.
As discovered by Dr. Henry Rawle Geyelin, when a body is fasting, glucose levels in the blood drop, while at the same time, the levels of ketones increase.
When the body burns ketones for fuel rather than glucose, there is less stress on the brain, reducing the onset of epileptic seizures.
Anyway, enough of the history lesson, let me explain how it works.
Getting Into Ketosis
When consumed in foods, carbs convert into glucose, the energy source that powers the body and the brain in the bloodstream.
Now, the body is in a state of ketosis. The liver will convert fats into fatty acids and ketones, which replace glucose to produce energy.
To reach this state of ketosis, most of what you eat will contain a high amount of fats and a moderate amount of protein. You will also severely restrict your carbohydrate intake.
When you restrict your net carbohydrates to around 5% of your calorie intake, around 20 to 30 grams per day (which requires you to limit the intake of many common foods), your body will soon become super-efficient at burning fat for energy.
Studies have also shown that once the body is in a state of ketosis, it can run 70% more efficiently as these ketones are the preferred energy source over glucose (carbs).
The first aim of starting the diet is to deplete the body's glycogen stores. These are the ways the body processes and stores glucose as energy.
When you do high-intensity exercise like running, the muscles draw upon the glycogen stores for fuel. For this reason, long-distance runners do "carb-loading" before significant events.
In the liver, the glycogen keeps the body functioning correctly all day, including brain function, kidney cells, and red blood cells.
Glycogen depletion is typically brought on by switching to a low-carb diet like the keto diet. You will feel the side effects of this in the first few days, as you'll read about later in the article. To fully deplete the body's glycogen stores, it takes typically 2 to 3 days.
Each gram of glycogen is also bound to 3 to 4 grams of water. So, by depleting your glycogen, excess water weight is flushed from your body.
Starting On Keto
When first starting the keto diet, counting calories is not what you should be concerned with. Calorie counting is one of the main reasons people begin to lose interest and quit.
The recipes in this keto diet meal plan are structured to offer the best basis for achieving your goals. A low-carb diet menu with delicious meals that don't make you feel like you're eating bland food is crucial for success.
Not only are there recipes for breakfast, lunch, dinner, and dessert, but plenty of snack recipes are included that you can enjoy between your main meals.
All these will help you feel full and satisfied, so you have less intention of giving up. Although the recipes are arranged for each day and week, mixing and matching your favorite recipes is possible!
We have everything from sumptuous smoothies to no-bake cheesecakes and tortilla chips for a night on the sofa!
Even pancakes and easy-to-make ice cream will stop you from feeling deprived of your favorite foods!
All the meals have a limited carb count, which should help you to reach a state of ketosis most quickly with the minimum amount of effort. Remember, you can mix and match your favorite recipes. The choice is yours.
Foods to Eat on Keto
Here is a chart of keto-friendly foods that can be included in your low-carb eating plan. When buying low-carb or keto-branded food, always check the nutritional information to ensure they are genuinely low-carb and keto-friendly.

Foods to Avoid on Keto
Before we start on what foods to avoid, if you are an athlete or very athletic, your daily intake will be quite different from that of an average person.
Highly active people must adjust their calorie intake to support their exercise regime.
Although protein is not to be avoided while on the keto diet, it will still have to be eaten in moderation, consuming high amounts of protein can raise the body's insulin levels while lowering your ketone levels.
A safe estimation of the amount of protein consumed daily is around 20% to 25% of your daily calorie intake.
Not all fats are equal, and any oils high in polyunsaturated fats (Omega-6), such as soy, safflower, and cottonseed, should be avoided.
These sources also include salad dressings and some types of mayonnaise.
- Factory-farmed Meat: Factory-farmed meats and fish contain high amounts of Omega-6 and other chemicals that can harm humans.
- Liquid Eggs: Liquid eggs contain many additives and often contain fructose corn syrup, which contains many carbs.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Artificial sweeteners as a replacement for sugar may be OK, but they can induce cravings and have no health benefits.
- Fresh Milk: Fresh milk should be consumed in moderation. We believe fresh milk is good for us, but as most milk is pasteurized, all the good bacteria have been killed off. Another thing you may not realize is milk has a high carb count. One cup contains about 12 grams of carbs. Use unsweetened almond or coconut milk as an alternative, or if you are drinking tea or coffee, try to use a bit of cream instead.
- Sweetened foods: Sweetened foods and drinks should be avoided.
- Legumes/Beans: Legumes and beans are staple foods in standard diets. They both should be avoided, along with lentils, kidney beans, and chickpeas.
- Fruits: Fruits can contain high levels of sugar. Avoid grapes, tangerines, bananas, mangoes, pineapple, and all types of dried fruit. However, some fruits can be consumed on keto. Small portions of berries are OK (blackberries, raspberries, blueberries, etc.) Here is our complete guide to keto fruits with a printable chart.
- Grains/starches: Starches and grains are in most of what we eat, and most of our current diet will consist of these in one form or another. The foods to avoid include rice, bread, pasta, wheat-based cereals, crackers, cookies, and Pizza.
- Root vegetables: Root vegetables are some of the main culprits. Potatoes, carrots, parsnips, etc., should all be avoided.
- Condiments: Ketchup and sauces are highly processed and contain added sugars, unhealthy fats, and other additives. Ketchup, for instance, contains 5 grams of carbs per tablespoon, whereas honey mustard contains 11 grams per sachet. We've put together a post on the best keto condiments for your keto diet.
- Alcohol: Alcohol is made from grains, and you guessed it, carbs are present in grains. But don't worry! There are lots of alcoholic beverages you can enjoy on a keto diet. We've put together a complete keto alcohol guide and the best low-carb alcoholic drinks that won't affect your diet. You can also check out our roundup of keto cocktails with a ton of cocktail recipes you can make at home.
- Sauces: Avoid gravy or packet sauces containing flour or sugar. Either choose low-carb versions or make your own
- Yogurt: Flavored yogurts can contain up to 30 grams of carbs per 6-oz serving. A better option is Greek yogurt, which only contains around 6 grams of carbs per 6-oz serving.
- Coleslaw: A small serving of coleslaw can contain up to 14 grams of carbs.
- Peanut butter: Sweetened peanut butter can contain very high amounts of sugar, which makes its carb content high. 100% natural peanut butter is an excellent choice on keto. Each tablespoon contains 3 grams of carbs with 1 gram of fiber, with only 2 grams of net carbs. Almond butter, hazelnut butter, and pili butter are also great on keto.
- Balsamic oil: Salad dressings can have varying amounts of carbs. Some fat-free options can contain up to 12 grams per serving. Always check the ingredients in sauces and condiments.
- Fried foods: Chicken nuggets and sandwiches from some of the more popular chains contain 10-50 grams of carbs.
- Low-fat/Diet products: Lastly, one that defies all logic, low-fat or diet products, even some sugar-free diet foods, are highly processed and contain many carbs. For low-fat dressings, food manufacturers typically replace fats with sugars to maintain flavor. Stay with full-fat versions, but limit your portion size.
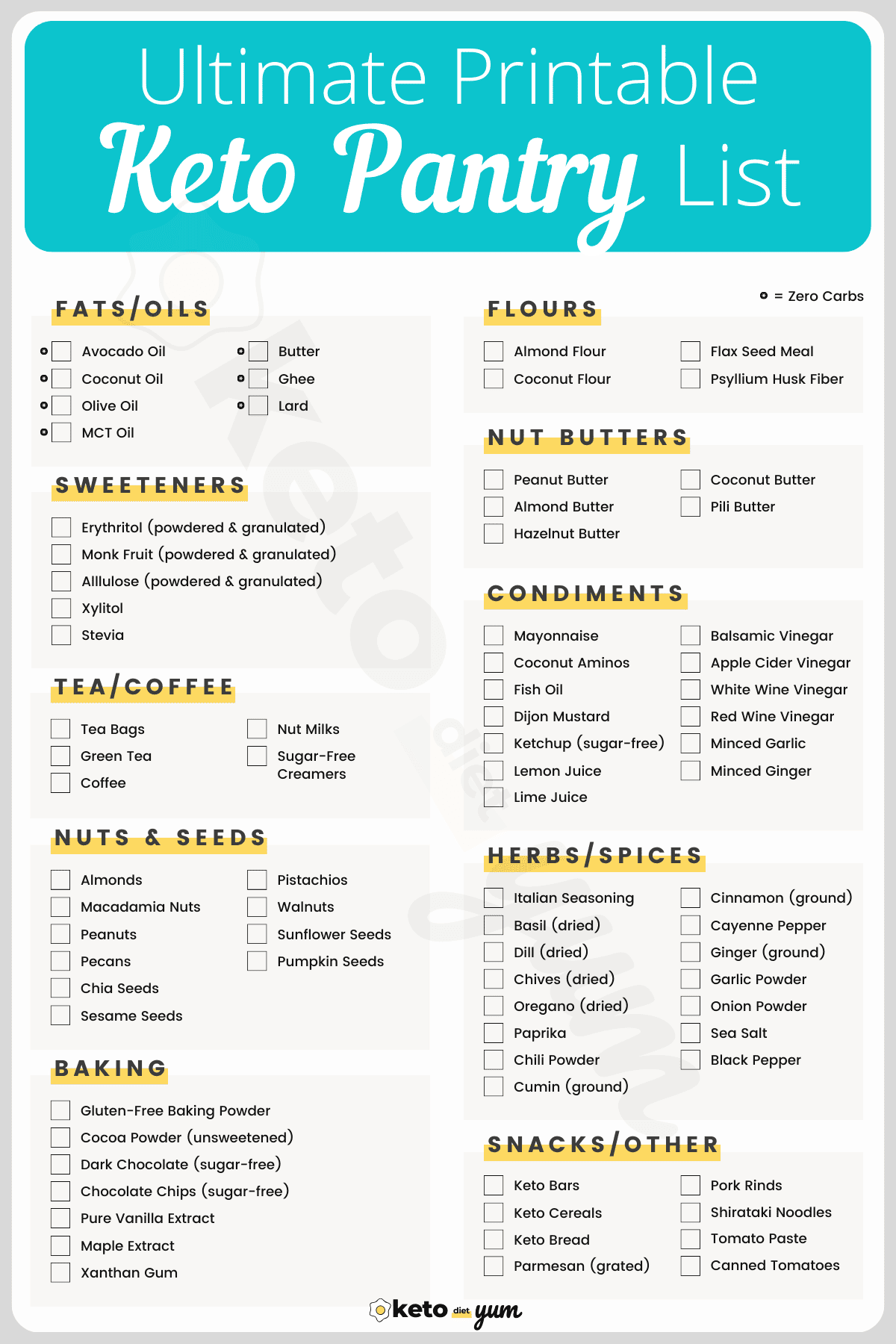
Essential Groceries List
While on the keto diet, your shopping habits will change, as will most of the contents in your kitchen and pantry. The list below is by no means complete. The aim is to give you a good starting point for what items you should be considering stocking, what is available, and what you should avoid.
The best advice is to eat various fresh meat, wild-caught seafood, plenty of fresh vegetables, and natural fats that have not been processed. If used in moderation, some canned goods can be used as long as they are not processed meals.
Most of the items below should be in stock in your kitchen.
Fats and Oils
- Avocado oil
- Coconut oil
- Olive oil
- MCT oil
- Butter
- Ghee
- Lard
Sugar-Free Sweeteners
- Erythritol: Powdered and granulated.
- Monk fruit: Powdered and granulated.
- Allulose: Powdered and granulated.
- Xylitol
- Stevia: Powdered and liquid.
Snacks and Other
- Meat snacks: Types of jerky with no added sugar.
- Pork rinds: Use these as an alternative to breadcrumbs, or sprinkle them on salads and soups to add flavor.
- Canned tomatoes: Check for no added sugars and get the lowest carb content.
- Tomato paste: Check for added thickeners or added sugars.
- Nut butter: Unsweetened peanut butter, almond butter, hazelnut butter, pili butter, and coconut butter.
Baking Ingredients
- Flour substitutes: Almond flour, coconut flour, flax seed meal, and psyllium husk fiber.
- Extracts: Pure vanilla extract and maple extract.
- Whey: Protein powder is excellent in baking and smoothies, so have some flavored and plain whey in your pantry.
- Chocolate: Sugar-free dark chocolate, chocolate chips, and unsweetened cocoa powder.
- Baking: Gluten-free baking powder, baking soda, and xanthan gum.
- Stock: Chicken, beef, and vegetable stock with no added sugars.
Condiments
- Mayonnaise
- Coconut aminos
- Fish oil
- Dijon mustard
- Ketchup (sugar-free)
- B.B.Q. sauce (sugar-free)
- Lemon juice
- Lime juice
- Balsamic vinegar
- Apple cider vinegar
- White wine vinegar
- Red wine vinegar
- Minced garlic
- Mince ginger
- Capers
Herbs and Spices
Herbs and spices are one way you can transform the taste of your meals, although you should always check their contents to ensure they contain no sweeteners.
- Italian seasoning
- Dried basil
- Dried dill
- Dried chives
- Dried Oregano
- Ground ginger
- Garlic powder
- Onion powder
- Paprika
- Chili powder
- Ground cumin
- Ground cinnamon
- Cayenne pepper
- Sea salt
- Black pepper
- Red pepper flakes
Nuts and Seeds
Although these are on your pantry list and a great source of Omega 6 fatty acids, nuts contain carbs and don't take much to add up.
- Almonds
- Macadamia nuts
- Peanuts
- Pecans
- Chia seeds
- Hazelnuts
- Sesame seeds
- Pistachios
- Walnuts
- Sunflower seeds
- Pumpkin seeds
Vegetables
With vegetables, it is best to stick to green, leafy veggies and avoid any root vegetables.
- Lettuce
- Kale
- Spinach
- Bok choy
- Cabbage
- Asparagus
- Artichokes
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Cauliflower
- Celery
- Cucumber
- Garlic
- Green beans
- Mushrooms
- Onions
- Bell peppers
- Pumpkin
- Radish
- Sauerkraut
- Spaghetti squash
- Zucchini
Meat and Poultry
When buying meat, try to get grass-fed and organic. Pesticides or antibiotics will not be used on these animals. Another category of meats is organ meats. Although not popular with a lot of people, they are one of the most nutritious foods available.
- Poultry: All types of chicken and turkey.
- Beef: All cuts (chops, steaks, ribs, ground, etc.)
- Pork: All cuts (chops, steaks, ribs, roast, bacon, ground, etc.)
- Lamb: All cuts (chops, roast, etc.)
- Game meat: Venison, buffalo, etc.
- Organ meat: Heart, liver, kidney, tongue, tripe, etc.
- Deli meat: Salami, pepperoni, prosciutto, pastrami, cold cuts, etc.
Seafood and Shellfish
Although more expensive, fish and shellfish have more nutrients and can be a great alternative to meat and poultry.
- Fish: Bass, cod, haddock, halibut, herring, mackerel, tuna, tilapia, trout, salmon, etc.
- Shellfish: Mussels, oysters, clams, scallops, shrimp, crab, prawns, lobster, etc.
- Canned: Canned fish in oil or brine is great for keto. Ensure it has no added sauce—canned tuna, salmon, crab, etc.
Eggs, Dairy, and Milk Substitutes
- Hard cheese (Parmesan, cheddar, etc.)
- Soft cheese (Feta, brie, ricotta, cream cheese, cottage cheese, etc.)
- Heavy cream
- Sour cream
- Butter
- Unsweetened almond milk
- Unsweetened coconut milk
Fruit
- Avocado
- Blackberries
- Blueberries
- Coconut
- Lemon
- Limes
- Green olives
- Raspberries
- Strawberries
- Tomatoes
Beverages
As with most drinks, it is better to check the ingredients for any hidden sugars they may contain.
- Water
- Soda water
- Tea (normal & herbal)
- Sparking mineral water
- Coffee (black)
Here is an easy printable pantry list PDF to help keep things simple when shopping. Sign up below and get it sent straight to your email!
Exercising on the Keto Diet
Strictly speaking, there is no reason why you need to exercise while on the keto diet. To lose weight, one must eat a diet that will do all the work.
However, there are lots of reasons to incorporate exercise into your diet. There are many great benefits to your health, including:
- Improved bone mineral density: Studies show that resistance training improves bone mineral density in obese postmenopausal women.
- Improved immunity: Exercise may help you boost your immune system. Keep in mind that over-exercising will have the opposite effect.
- Improving diabetes by increasing insulin sensitivity: Moderate aerobic exercise lowers blood sugar, and adding one 10-second sprint after moderate-intensity aerobic exercise can reduce hypoglycemia risk in physically active individuals with type 1 diabetes.
- Brain Health: Exercise improves age-related cognitive decline and helps prevent neurodegenerative diseases.
- Cardiovascular health: Vigorous and moderate physical activity helps prevent coronary heart disease.
- Anti-aging benefits: Exercise may increase life expectancy by decreasing mortality risk factors like high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, stroke, and cancer. Exercise isn’t just to burn calories to aid in weight loss. Exercise should promote muscle tone and help you feel good about yourself, so whatever activity you do, do it for pleasure. If you contemplate any exercise, you should allow plenty of rest between sessions. Due to the lack of carbs, you may overdo it and be prone to dizzy spells until you have become accustomed to the diet properly.
Dining Out Tips on Keto
Dining out, especially at fast food joints, could seem a bit daunting, but you have options that you may not realize you have. I will review some of the more common places and what is available for you.
- McDonald's/Burger King: Both McDonald's and Burger King offer items that can be made low-carb at a low price. You can order a breakfast sandwich at either restaurant and order without the bun. The same goes for a grilled chicken breast or burger for lunch or dinner. My personal favorite is the McDouble from McDonald's Value Menu. Just forget the bun and the ketchup. It is delicious and keto-friendly at only 4g carbs.
- Kentucky Fried Chicken: KFC is a great place to stop for a meal. Each serving of their grilled chicken is either only 0 or 1g of carbs. Ordering a few pieces of grilled chicken is super simple and super quick. Just remember to skip most sides and ketchup, but if you must have one, order an individual serving of green beans, which is only 2g net carbs. If you prefer a salad, order without dressing; it will only be around 2g of carbs.
- Taco Bell: You may be able to order just the side dishes. The chicken, beef, lettuce, and guacamole come in cheap, and the carbs are pretty decent.
- Gas stations: Many gas stations offer eggs, deli meat, and string cheeses, which can be a viable option. Also, if they sell a breakfast sandwich, discard the bun, leaving you with tasty sausage, egg, and cheese.
- Wendy's: Their double stack order without a bun has just 4g carbs. It is also easy on the wallet. They also have the ultimate chicken grill sandwich, 5g carbs without the bun.
- In-N-Out Burger: If you are lucky enough to live close to these guys, they will supply a burger without a bun, but instead of a bun, they will supply it in a lettuce wrap. Just swap the house spread and replace it with mustard and extra pickles.
- Chipotle: Fancy Mexican? For spicy food, this is probably your best bet. Order the burrito bowl without rice, or they have a wonderful salad. The meat, cheese, sour cream, lettuce, and salsa cost extra, but it can be worth the little extra to be satisfied with some wholesome food without fearing overstepping your carb mark.
- Unwich: All their sandwiches can be ordered without bread or tortillas. They’ll replace it with a lettuce wrap. You can order online and check your carbs as you go.
- Five Guys Burger and Fries: These guys will supply your burger without a bun or any hassle. They will provide a lettuce wrap, or you can take it 'to-go' in an aluminum tray. You can also pick your toppings from their menu board. They also give extra cheese and bacon at no additional charge. If you find yourself dining in, they also have peanuts in the shell that you can nibble on while waiting for your burger.
Benefits of a Keto Diet
Over the decades, there has been much discussion about low-carb diets. Since 2002, there have been over 20 human studies on diets of this sort, and it is a low-carb diet that consistently comes out on top.
I will explain the top 11 advantages of following a ketogenic diet plan. Not only is weight loss affected, but you will also find many other health benefits it can bring you.
- You'll Feel Less Hungry
Dieting makes you hungry, which is the main reason people end up miserable and quitting their diet. But with the keto diet, you automatically have a reduction in appetite.
Studies show that people who eat more fat and protein eat fewer calories. They feel less hungry than on most other diets.
- You'll Have More Sustainable Weight Loss
While these studies show you become less hungry by following a low-carb diet, they also concluded that you could lose more weight and lose weight faster than people on low-fat diets.
Even if the ones on a low-fat diet restrict their calorie intake, the keto diet will eliminate excess water from the body over the first couple of weeks.
Insulin levels become lower due to the restriction of carbohydrate intake, which allows the kidneys to start removing excess sodium. Lower sodium can help lead to rapid weight loss in the first week or two.
It has also been shown that the weight loss achieved when following a keto diet can be 2 to 3 times more than when following a low-fat diet. That’s all without feeling hungry! Wouldn’t you say that is a significant advantage?
- You'll Lose More Belly Fat
Not all fat in the body is the same, and the location of these fat deposits dictates what disease you will be prone to, but unfortunately, when on a diet, the body decides where to take the fat from.
Luckily, the keto diet reduces more fat from around the abdomen. The most important thing to know is we have fat under the skin and then fat in the abdominal cavity, which builds up around the internal organs.
This fat build-up can increase inflammation and insulin resistance and is one of the significant factors of metabolic dysfunction, which is most common in today's Western diet.
Luckily, the keto diet is super-efficient at reducing internal body fat, which helps to reduce the risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
The amount of weight loss that any one person can lose will vary. However, tests conducted by the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition showed men who followed the ketogenic diet for four weeks lost an average of 12 pounds.
They could also eat fewer calories without the hunger generally associated with regular diets.
- A Reduction of Triglycerides (Fat Molecules)
You will be pleased to know low-carb diets are very effective at lowering the levels of triglycerides in the blood. These fat molecules increase the risk of heart disease.
The leading cause of high triglyceride levels is carbohydrate consumption. So, as you reduce your carbohydrate consumption, the levels of these triglycerides in the blood are also reduced.
It should also be noted that people who follow a low-fat diet can suffer from increased triglyceride levels.
- Increased HDL Levels (Good Cholesterol)
HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein) is often referred to as good cholesterol, and it is HDL that carries cholesterol away from the body to the liver, where it gets flushed from the system or re-used.
It is also known that higher HDL levels make you less prone to the risk of heart disease. Another indicator that can show if a person is prone to heart disease is the Triglycerides to HDL ratio. The higher it is, the greater the risk.
Following a ketogenic diet, this ratio can improve significantly as HDL levels are raised while triglyceride levels are lowered.
- Lowered LDL Levels (Bad Cholesterol)
LDL is the opposite of HDL and is referred to as bad cholesterol. High LDL levels can lead to heart disease.
Studies have also shown that the size of the LDL particles is essential. Small particles give the most significant risk, whereas larger particles give a lower risk. Once again, the keto diet helps with this.
By following a low-carb diet, the particles of LDL change from small to large, thus reducing the number that can float around the body.
- Improved Blood Sugar and Insulin Levels
When carbs are consumed, the body breaks these down, and they get converted into simple sugars, namely glucose, by the digestive system.
Upon entering the bloodstream, these simple sugars raise blood sugar levels. Our bodies produce the hormone insulin to combat and maintain blood sugar levels.
In ordinary people, this increased amount of insulin is not much of a problem, but in people with insulin resistance, it is a significant problem. It can lead to type 2 diabetes, and figures for people with this problem are currently over 300 million worldwide.
The keto diet can provide you with the solution to this. By reducing carb intake, the body does not have to produce as much insulin, as the blood sugar levels from a reduction in carbs are significantly reduced.
Studies have also shown people with diabetes can reduce the need for medication within six months by following the keto diet. It should be noted if you are currently on medication, you should consult your doctor before proceeding.
- Lowered Blood Pressure
High blood pressure (hypertension) can be the root of many human illnesses. These can include kidney failure, strokes, and heart disease, to name but a few.
The keto diet is a very effective way of reducing blood pressure and lowering the risk of these illnesses.
- Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic Syndrome is a collection of symptoms that can lead to diabetes and heart disease.
These symptoms range from Abdominal obesity, high blood sugar levels, low HDL levels, and high triglycerides. Although these can be serious, they can all be reduced by following the keto diet.
- Improved Brain Functions
Initially, the keto diet was introduced to help treat children who had epilepsy.
This was something the keto diet had many successful results in achieving. Over 50 % of children treated showed a 50% reduction in seizures, while 16% stopped having seizures altogether.
Some parts of the brain can only burn glucose, as the carb intake is reduced on the keto diet. The liver converts protein to glucose, which can supply these parts of the brain. Ketones power the other parts of the brain.
These are produced when the body is starved of carbs. This is the main reason the keto diet is so successful at treating epilepsy.
Not only that, more recent studies have shown the keto diet can be helpful in other forms of brain disorders, namely Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's Disease.
- Cancer
Research has shown sugar is the primary fuel that can feed cancer cells. The cancer cells ferment the sugars to produce oxygen. This, in turn, increases the amount of inflammation in the body.
Dr. Otto Warburg discovered this in the 1930s. He also found that when the body has low blood sugar content, the inflammation is reduced, and the cancer cells cannot thrive as the blood is fully oxygenated naturally.
Keto Meal Plan Breakdown
Stage 1 of our free keto diet plan will be the first strict five days, where we will force our bodies into ketosis.
Stage 2 is the next two weeks of the diet (days 6-19), where we lighten up on restrictions and experience incredible benefits!
The First 5 Days Of Keto
The keto diet has a few side effects that may happen in the first five days. As with any diet, these are normal and will quickly pass after a couple of days.
There will also be a difference if the diet is for children or adults. Most of these side effects are manageable if you understand why they happen.
This knowledge beforehand means you can minimize the effects and are less likely to quit.
It only takes a short time for your body to enter a state of ketosis; from this point, the side effects will subside as it adapts to burning fat for energy rather than glucose.
Please always, always seek medical advice before you start. Prioritize your health for safety and long-term longevity.
- Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
As your body is used to a high-carb diet, it creates insulin to counteract the sugar from your carbohydrate intake.
Once your carb quantity drops on the keto diet, you may experience low blood sugar episodes. Symptoms include:
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Feeling shaky
- Hunger
- Headaches
- Irritability
- Pounding heart (racing pulse)
- Pale skin
- Sweating
- Trembling
- Weakness
- Anxiety
It can seem scary if you have not experienced it before. The easiest way to maintain this is by taking glucose tablets, so when you feel this is about to happen, take one or two tablets, which should be enough to prevent this from happening.
- Keto Flu / Headaches
Also known as 'keto flu,' any significant change in diet can cause headaches for no apparent reason. You may become lightheaded and have flu-like symptoms that can occur over several days.
These headaches happen as there is a mineral imbalance due to diet changes. The best way to resolve this quickly is to add one-quarter of a teaspoon of salt into a glass of water and drink. You should sit down for 15 – 20 minutes for the effects to work.
To prevent this from happening, you should drink plenty of water and increase your salt intake for the first few days. This can effectively stop the chance of headaches.
- Fatigue and Dizziness
Your body will start losing stored water, so this must be replaced. As a result, you will lose many minerals over the first week of the diet.
With low minerals, you may feel tired, dizzy, and lightheaded, along with the chance of getting unwanted muscle cramps - and a possibility of itchy skin.
To combat these effects, increase the amount of green leafy vegetables you consume.
Or, as a backup, it is possible to use multivitamin tablets that provide the recommended daily allowance for the lost minerals you require. Stay clear of any vegetables high in carbs, as discussed earlier.
- Constipation
This is one of the most common side effects. This comes from losing fluids and becoming dehydrated, loss of salt, a magnesium deficiency, or too many dairy/nut products.
If things don't change by taking vitamin tablets (to improve your magnesium intake), you may have to reduce your dairy product intake even more.
- Diarrhea
Thankfully, these symptoms typically only last for a few days. Once you have increased your fat content, your body should adjust, and these symptoms should subside.
Always drink lots of water to replace the lost fluids so as not to become dehydrated.
- Interrupted Sleep Patterns
Some people mention they have problems sleeping while on the keto diet - if this happens, it can be a sign your insulin levels are low.
To solve this, have a small snack containing equal protein and carbs before bed. This will help balance your insulin level for the short term for the night.
- Heart Palpitations
This can happen to some people and not happen to others, like if you drink a strong cup of coffee.
However, while on the keto diet, it can be a sign a person has low blood pressure. Always seek medical advice if you are not sure.
- Sugar Cravings
This is one of the most challenging side effects to resist. Give yourself time, and these will subside from a few days up to around 21 days.
Some ways to combat these cravings are doing light exercises or finding something that can occupy your mind.
Sugar cravings will only last for an hour, so this will have gone by the time you have completed your exercise.
You can also have a snack consisting of a few ounces of protein, either as a small salad or a small, quick-to-prepare keto smoothie recipe.
Again, a child should NEVER be placed on a ketogenic diet. The consequences are very drastic and harmful while children are still growing. It is better to give them all the fruits, vegetables, carbs, and proteins in a balanced diet and limit the processed sugar in candy, sodas, and sweets.
Stage 1: Week 1 (Days 1-5)
So, now that you know what to expect, you're ready for Stage 1 of our keto diet plan for beginners.
Follow the recipes for each day, and feel free to mix and match your favorites if you don't like a particular meal.
Add a couple of snacks each day, depending on your hunger.
If you're unsure how much food you should consume, read our keto calories guide for an in-depth guide on calories and macronutrients.
Each recipe has the number of servings and the number of calories and net carbs, so you'll be able to calculate how much you should be eating each day.
The recipes in your Stage 1 diet are designed to be as low on carbs as possible (limiting it to no more than 30 grams per day) so that you will quickly deplete your glycogen stores and reach a state of ketosis.
This can happen as fast as 48 hours, so five days should guarantee you'll get there.
We "lighten up" on the carb intake in Stage 2 so that your food options become less restrictive.
Each day's recipes range between 1600 to 1850 calories, with a maximum of 30 grams of net carbs.
As mentioned above, please use the keto calorie calculator and adjust the servings and snacks of the meal plan to suit your goals.
A shopping list is at the end of this easy keto meal plan to help you prepare for the first stage of the diet. (This is currently being updated, sorry!)
BURN UP to 20 pounds
The Ultimate Keto Kickstart Bundle is your all-in-one digital guide for mastering the ketogenic lifestyle. This 59-page printable PDF provides essential resources, practical tools, and delicious meal plans designed for both beginners and experienced keto followers. Whether you're just starting your low-carb journey or looking to refine your approach, this bundle offers comprehensive guidance, meal ideas, and strategies to help you achieve your health and weight loss goals.
Health Disclaimer: A ketogenic or keto diet has many proven benefits, but it is still controversial. Any information we provide is for your personal use and for educational purposes only. Always consult with your doctor before beginning any diet or nutrition routine, especially if you are pregnant or have any pre-existing health conditions. Nothing contained on this website should be considered medical advice.
Day 1
- Breakfast - Egg Muffins (2 servings)
- Snack - Zucchini Chips (1 serving)
- Lunch - B.L.T Salad (1 serving)
- Snack - Peanut Butter Cookies (1 serving)
- Dinner - Meatloaf (2 servings) and Cauliflower Mash (1 serving)
- Summary - 1670 calories and 19 grams of net carbs
Day 2
- Breakfast - Cranberry Pancakes (1 serving)
- Snack - Crispy Crackers (6 servings)
- Lunch - Deviled Egg Salad (1 serving)
- Snack - Raspberry Cheesecake Bites (4 servings)
- Dinner - Chicken Pad Thai (1 serving)
- Summary - 1628 calories and 19.5 grams of net carbs
Day 3
- Breakfast - Pumpkin Pancakes (2 servings)
- Snack - Peanut Butter Mousse (1 serving)
- Lunch - BLT Salad (1 serving)
- Snack - Tortilla Chips (2 servings)
- Dinner - Shepherd's Pie (1 serving)
- Summary - 1554 calories and 27.9 grams of net carbs
Day 4
- Breakfast - Chaffles (2 servings) + Crispy Bacon (2 servings)
- Snack - Cheesecake Fat Bombs (3 servings)
- Lunch - Lahmacun (Turkish Pizza) (2 servings)
- Snack - Tortilla Chips (2 servings)
- Dinner - Chicken Meatballs with Zoodles (1 serving)
- Summary - 1760 calories and 27 grams of net carbs
Day 5
- Breakfast - Fathead Bagels (2 servings)
- Snack - Crispy Parmesan Crackers (2 servings)
- Lunch - Salad with Italian Dressing (1 serving)
- Snack - Cheesecake Fat Bombs (3 servings)
- Dinner - Zucchini Alfredo (1 serving)
- Summary - 1819 calories and 21.8 grams of net carbs
Stage 1: Week 1 Snacks
Stage 2: Week 2 (Days 6-12)
Congratulations! You've made it through Stage 1's first five days.
You'll find that the recipes for the next two weeks are perhaps a little more balanced in the macros.
Have fun with it!
Follow the recipes as is, or mix and match if you like.
Make the ones you like again and skip the ones you don't.
Day 6
- Breakfast - Cranberry Pancakes (1 serving)
- Snack - Chocolate Mousse (1 serving)
- Lunch - Iceberg Wedge Salad (1 serving)
- Snack- Crispy Parmesan Crackers (2 servings)
- Dinner - Garlic Butter Chicken (1 serving)
- Summary - 1729 calories and 22.5 grams of net carbs
Day 7
- Breakfast - Egg Muffins (2 servings)
- Snack - Coconut Cookies (2 servings)
- Lunch - Cauliflower Pizza (2 servings)
- Dinner - Meatloaf (3 servings) + Homemade Keto Ice Cream (1 serving)
- Summary - 1772 calories and 31.8 grams of net carbs
Day 8
- Breakfast - Almond Flour Banana Bread (2 servings)
- Snack - Cream Cheese Lemon Fat Bombs (3 servings)
- Lunch - Fish Cakes with Garlic Aioli (2 servings)
- Snack - Avocado Smoothie (1 serving)
- Dinner - Almond Flour Pizza with Feta and Bacon (2 servings)
- Summary - 1812 calories and 21.2 grams of net carbs
Day 9
- Breakfast - Keto Chia Seed Pudding (1 serving)
- Snack - No-Bake Peanut Butter Energy Balls (2 servings)
- Lunch - Keto Lettuce Wraps (2 servings)
- Snack - Almond Flour Banana Bread (2 servings)
- Dinner - Roast Chicken with Broccoli & Garlic Cheese (1 serving)
- Summary - 1697 calories and 25.21 grams of net carbs
Day 10
- Breakfast - Easy Zucchini Bread (2 servings)
- Lunch - Tuna Cucumber Cups (2 servings)
- Snack - No-Bake Peanut Butter Energy Balls (2 servings)
- Dinner - Beef Stroganoff (1 serving) + Keto Gelato Bars (2 servings)
- Summary - 1573 calories and 30 grams of net carbs
Day 11
- Breakfast - Baked Avocado Egg Boats (2 servings)
- Snack - Keto Donut Holes (4 servings)
- Lunch - Creamy Pumpkin Soup (1 serving)
- Dinner - Easy Balsamic Chicken (1 serving) + Baked Zucchini Fries (1 serving)
- Summary - 1738 calories and 2.9 grams of net carbs
Day 12
- Breakfast - Healthy Pumpkin Bars (2 servings)
- Snack - Keto Donut Holes (4 servings)
- Lunch - Raspberry Cheesecake Smoothie (1 serving)
- Snack - Peanut Butter Cookies (3 servings)
- Dinner - Caprese Chicken (1 serving) + Baked Zucchini Fries (1 serving)
- Summary - 1830 calories and 30 grams of net carbs
Stage 2: Week 2 Snacks
Stage 2: Week 3 (Days 13-19)
OK, now you should be getting a good hang of it, and I am sure if you followed the diet to a 'T,' you would have seen results by now.
So, let's hope this keeps you motivated and ready to enjoy our recipes for week 3.
Day 13
- Breakfast - Keto Crepes (1 serving)
- Snack - Peanut Butter Cookies (2 servings)
- Lunch - Vegetarian Cauliflower Sushi (2 servings)
- Snack - No-Bake Peanut Butter Energy Balls (2 servings)
- Dinner - Chinese Orange Beef (2 servings)
- Summary - 1803 calories and 25.8 grams of net carbs
Day 14
- Breakfast - Keto Egg Loaf (2 servings)
- Snack - Baked Zucchini Balls (4 servings)
- Lunch - Keto Peanut Butter Smoothie (1 serving)
- Dinner - Lemon Garlic Salmon (1 serving) + Pumpkin Mousse (1 serving)
- Summary - 1649 calories and 22 grams of net carbs
Day 15
- Breakfast - Keto Egg Muffins (2 servings)
- Snack - Avocado Brownies (2 servings)
- Lunch - Deviled Egg Salad (1 serving)
- Dinner - Eggplant Casserole (2 servings) + No-Bake Cheesecake (1 serving)
- Summary - 1596 calories and 25.9 grams of net carbs
Day 16
- Breakfast - Fathead Bagels (2 servings)
- Snack - Parmesan Croutons (1 serving)
- Lunch - Halloumi Salad (1 serving)
- Dinner - Pan-Seared Salmon with Goat Cheese (1 serving) + No-Bake Cheesecake (1 serving)
- Summary - 1845 calories and 20.5 grams of net carbs
Day 17
- Breakfast - Leek and Bacon Omelette (1 serving)
- Lunch - BLT Salad with Avocado & Cheese (1 serving)
- Dinner - Baked Chicken with Yogurt & Lime (1 serving) + Loaded Cauliflower Mash (1 serving)
- Summary - 1828 calories and 21.5 grams of net carbs
Day 18
- Breakfast - Keto Crepes (1 serving)
- Snack - Cream Cheese Lemon Fat Bombs (3 servings)
- Lunch - Bacon Egg & Cheese Sliders (2 servings)
- Dinner - Baked Salmon and Green Beans (1 serving) + Keto Chocolate Cake (2 servings)
- Summary - 1673 calories and 25.8 grams of net carbs
Day 19
- Breakfast - Keto Chaffles (2 servings) + Crispy Bacon (2 servings)
- Snack - Pumpkin Spice Chocolate Chip Cookies (3 servings)
- Lunch - Cauliflower Salad (1 serving)
- Snack - Fathead Cinnamon Rolls (1 serving)
- Dinner - Ground Beef Cauliflower Curry (1 serving)
- Summary - 1594 calories and 30 grams of net carbs
Stage 2: Week 3 Snacks
Final Remarks
If you made it this far and are still reading, I would like to thank you very much!
The content I have provided you is a no-frills approach to everything you need to know while on the keto diet. It’s an excellent keto meal plan that is easy to follow and, best of all, FREE!
It can be a life-changing decision to undertake any diet, and I feel this information should be available to everyone who can benefit.
If you decide to try this meal plan, you will see I have based it on 19 days. Most people can commit to 19 days for their health, and I’m sure you will be surprised how much you can achieve.
I have also structured the meal plans with filling recipes and included snacks to minimize temptations and slip-ups as you start the diet.
The benefits of the ketogenic diet continue to be discovered over time, and it is not just a fad diet. It took nearly 100 years to arrive at the point we are now at, so it has undoubtedly stood the test of time.
Join the thousands of people who have already tried and benefited from the keto diet, and please leave a comment if you enjoyed this article!
We also have more keto meal plans available, including our keto intermittent fasting meal plan that combines the benefits of intermittent fasting with a ketosis diet plan.










Wow Nice, Thanks for sharing,
Love your article, very thorough and informative, TY. I started the keto program just shy of a year ago and have lost 91 lbs so far, not to shabby for a disabled 60 plus old... it's changed my life and health
Wow, Cee! That's incredible. I'm glad you're doing so well, that is a life-changing achievement!
A very informative and reflective article.It really helps me a lot.
Absolutely great article! I went to Nurse Practitioner conference that had a course “the ketogenic diet: it’s not just a fad” and was floored with all the health benefits. I continue to recommend keto to all my patients and follow it myself. Now I’ll have somewhere to direct my patients on how to get started!
My wife and I absolutely love your meal plans ans recipes. So nice to eat keto with recipes that taste like real food.
Hi Robert, so glad to hear that and thank you for the kind words!
thanks for shareing your great recipies i will be tryin some..look so delicious
Let me first thank you very much for the great source of information about keto diet plan. Your article really help me to understand better about this diet
Thanks for the detailed article
Can you do intermittent fasting and Keto at the same time?
Hi Scott, yes you can! We have a specific guide for combining intermittent fasting and keto here.
Hello there. I have a really bad egg intolerance so I cannot have eggs just by themselves. I also am not a fan of Avocados or tofu, is there something else that i can substitute with? Thank you so much that this article literally explains everything you need to know about this diet!
Hi Rene, you can just avoid the recipes that have the ingredients you don't like. You can just re-use the recipes you do like on the diet, there are no set rules 🙂
I'm determined to cook a delicious turkey this year for Thanksgiving. The last few years have been a real disappointment. For some reason I just can't get the bird to turn out moist and soft. Wish me luck!
Hey Emiko, I'm sure you'll love this recipe! Good luck!
I have read about keto, the meal plan is very good, and healthy, I like to place and order, to strared this program.
Thanks
Hi Octavia, than plan is completely free, you can start now just follow the recipes 🙂
I want to do this challenge but I saw there were recipes with salmon, I am not a fan of salmon. Is there a substitute I could use instead?
Honestly, if you tell me there isn’t a substitution for it in this challenge then I would do all that I could to suck it up and eat it. I just think that is one of the reasons most healthy lifestyle changes fail, people just get so wrapped around not liking the taste of the food that they stop or cheat.
Hi Kimberly! You can definitely avoid any of the salmon recipes on this meal plan.
You can actually just pick your favorite recipes and reuse them, there's no need to follow the recipes exactly as listed.
I've just provided a large number of recipes to pick from so that there's lots of options and so the meal plan doesn't seem too bland.
Hope that helps!
Jennifer thank you I love your recipes and so does my family! I usually make small adjustments or additions to make the meal more appropriate for my kids but for the most part your recipes and meal plan have greatly simplified my approach and ability to stick with keto
Have you ever considered selling your meal plan to an app or book? I would absolutely give either as a gift. Thanks again.
Hi Jessica! Thanks so much for the kind words. At the moment I'm not selling the meal plan and am happy to keep updating it and providing it for free 🙂
I have been considering making and ebook and app version for easier access when I have time!
Hi! Thank you so much for the recipes. Question. On the recipe it notes “net carb”. Do we use this number or the carb listed on the nutrition label?
Hi Alicia! Both of those should be the same, could you please let me know which recipe has different values? Thanks!
I was following the previous keto for beginners diet and bought all the ingredients for the week and now the recipes have disappeared and the whole menu has changed . Help does anyone have the recipes or know where I can get the previous one
Hi Shaquita, I've put up the old plan so that you can still access the recipes 🙂 https://www.ketodietyum.com/old-keto-meal-plan/
Excellent article with a set of practical guidelines. Keep up the good work, Jennifer. Three cheers for you.
Hello Jennifer. A couple questions.
On the menu you have the number of servings. I am thinking it means the number the recipe makes not what a person should eat.
Are we to eat only what you have listed? Like for the Philly cheesesteak, can we have a salad or veg with it?
Hi Shari!
Actually, the number of servings is what the person should eat. The recipe lists how many servings it makes and I've calculated that into that day's calories and carbs.
So for example, for the day 1 snack, the 4-seed crispy crackers recipe makes 15 servings (crackers) and you can eat 6 crackers.
For each day the meal plan lists exactly what to eat, so generally, you shouldn't be adding any extras with it. However, a simple salad contains almost no carbs or calories so should be fine.
Remember, the meal plan is just an example meal plan for a daily calorie intake of 1600-1850 calories. Your own needs may differ depending on how active you are so I suggest using the keto calorie calculator to determine how many calories you need to eat each day. Then you can adjust the servings or add snacks for your own goals.
Hope that helps!
Where can I find the calorie calculator?
Hey Laura, here's the calorie calculator.
Excellent info! I learned so much from this info and thanks for keeping it simple to understand. Starting today!
I was wondering if these recipes are good for the freezer. It will only be me doing keto in my house. I usually do a meal prep so if I can freeze some servings that would benefit me. Mainly the snacks and breakfasts.
Thank you for this, I have been hesitant to start this journey but this article is so helpful and makes me think I can do this
Hi Shannon. Most of the recipes are freezer-friendly. You can pick and choose the recipes so that you're only making freezable meals as well. Enjoy!
Hi Jennifer! Thank you for this site!! It is great to see wonderful human beings like yourself sharing your knowledge to help others. I love the Keto diet and I love your recipes as well. I now have a "meal plan" that taste like real food and that me and my husband can enjoy together. I would like to thank you again and keep on "Keto-ing"!!
Is there a vegetarian version of this plan?
Hi Terry!
This plan can easily be made vegetarian but you'll have to pick from my vegetarian recipes.
You can see all my keto vegetarian recipes here.
Choose whatever you like for breakfast/lunch/dinner/snacks and enjoy! I'll work on putting together a vegetarian outline soon.
Thanks!
Jennifer.
Hi Jennifer...have been following you for quite awhile and need this diet badly....not only am I overweight but also in bad health, so I need this. Question is...can I drink Coke Zero ....I gag on water and any form of milk and do not drink coffee or tea cause so bland and unsweetened. But this drink is my crutch and has held me back on many healthy steps..........thanks for your help.
Hi Mary!
Yes, you can drink coke zero, diet coke, or any other zero-sugar variety of drinks.
Jennifer.
Oh, thank you so much.....am ready to jump in.
Once you reach your weight loss goal what amount of carbs are allowed for not losing more weight but not gaining any back. Just to maintain your weight loss?
Hi Kelly!
Good question. If you are only using the keto diet to lose weight, you can increase your carb intake once you achieve your goals. If you wish to stay on the keto diet after losing weight, you must keep your carb intake the same.
The most important thing for not gaining weight back is consuming the right amount of calories. Here's how you can do that:
1. Use our keto calorie calculator and enter the weight you're aiming for.
2. The output will give you 'Calories to consume:,' which is the number of calories needed to maintain that weight.
From there, you can adjust the number of carbs in the 'Net carbs' box of the calculator to whatever number you'd like. By consuming more carbs, you'll be consuming less fat and protein.
I hope that helps!
Jennifer.
I am so excited to try the new 2023 menu! Thank you for all these recipes and menus!!
Thank you, Nancy! Wishing you the best of luck.
I have to tell you Jennifer, that I used your 2019 menu and started on keto. I lost 70lbs and most of those recipes are in our regular meal rotation still even now. That's why I am so excited to jump into this new plan and get more great recipes to use! Thanks again!
Hi Nancy!
That's absolutely amazing!!! Great job. I'm so glad you've had so much success on keto!
I hope you enjoy the new recipes as much as the old ones as well. Wishing you the best of luck.
Jennifer.
Hi Jennifer! I am 73 and would like to loose 20-25 lbs., so I am very excited to try this plan. Can I download this so it is in paper or book form?
Hi Sabra!
At the moment, the plan is only available on the website, but I'm working on getting it into an easy book.
I'll let you know when it's ready. Until then, I hope you're able to use the online version.
Jennifer.
Thank you for doing all of this work and sharing it without an obligation to subscribe to or purchase something. I'm wondering what the extra snacks are for at the end of each section.
Hi Amanda! Thanks for the kind words 🙂
The extra snacks are just additional options for your meal planning. You can mix and match your favorite recipes to make the diet easier to adhere to.
I hope that helps, and good luck!
Omg! This was so easy to read. Most other diets are so hard to figure out. I’m going to give it a try!! Thank you so much.
I am interested in starting the keto diet, I can not have any dairy, and I do not like avocados. Is that going to be a problem ?
Hi Lynda! There are plenty of recipes in the meal plan that are dairy free and don't use avocados. Just pick from those recipes, or take a look around the site and pick recipes that suit your diet. Hope that helps!
Thank you for making this information available for everyone. It is difficult to find good information online. Your page has inspired me to go on the Keto Diet now that I have a good understanding on it. I'm looking forward to trying out your recipes. Best wishes.
Do you have to eat 3 meals a day? I do better with only 2 meals and snack.
Hi CJ! You don't have to eat 3 meal per day, the meal plan is just a guide. You can easily eat 2 meals and a snack, just make sure you're consuming enough calories.
Can you switch out meals and snacks for the days if you don’t like certain items?
Yes, absolutely! The meal plan is just a guide and very flexible! You can mix and match your favorite recipes and meals. Just keep an eye on the calories and total net carb content for each day.